Ingesting Data
Viewing typescript
switch to python
Once you’ve defined a Data Model, Moose makes it easy to ingest data from data sources that align to the schema of your Data Model. Moose automatically spins up an API endpoint for each Data Model that you can make an HTTP POST request to with data that matches the schema of the Data Model.
For each Data Model, an ingestion API endpoint is spun up at:
http://localhost:4000/ingest/<DataModelName>For example, if you have a Data Model named Foo, the ingestion endpoint will be http://localhost:4000/ingest/Foo.
from moose_lib import moose_data_model, Key
from dataclasses import dataclass
@moose_data_model
@dataclass
class Foo:
primary_key: Key[str]
timestamp: float
optional_text: Optional[str]import { Key } from "@514labs/moose-lib";
export interface Foo {
primaryKey: Key<string>;
timestamp: number;
optionalText?: string;
}You can ingest data from any HTTP-compatible data source, including webhooks, scripts, and any existing application that can make an HTTP POST request.
OpenAPI Specification
Moose generates and automatically updates an OpenAPI specification for all API endpoints in your project. This specification is located in the openapi.yaml file in the root of your project. It provides a comprehensive overview of the available endpoints, request and response formats, and includes example data for each Data Model schema so you can quickly get started.
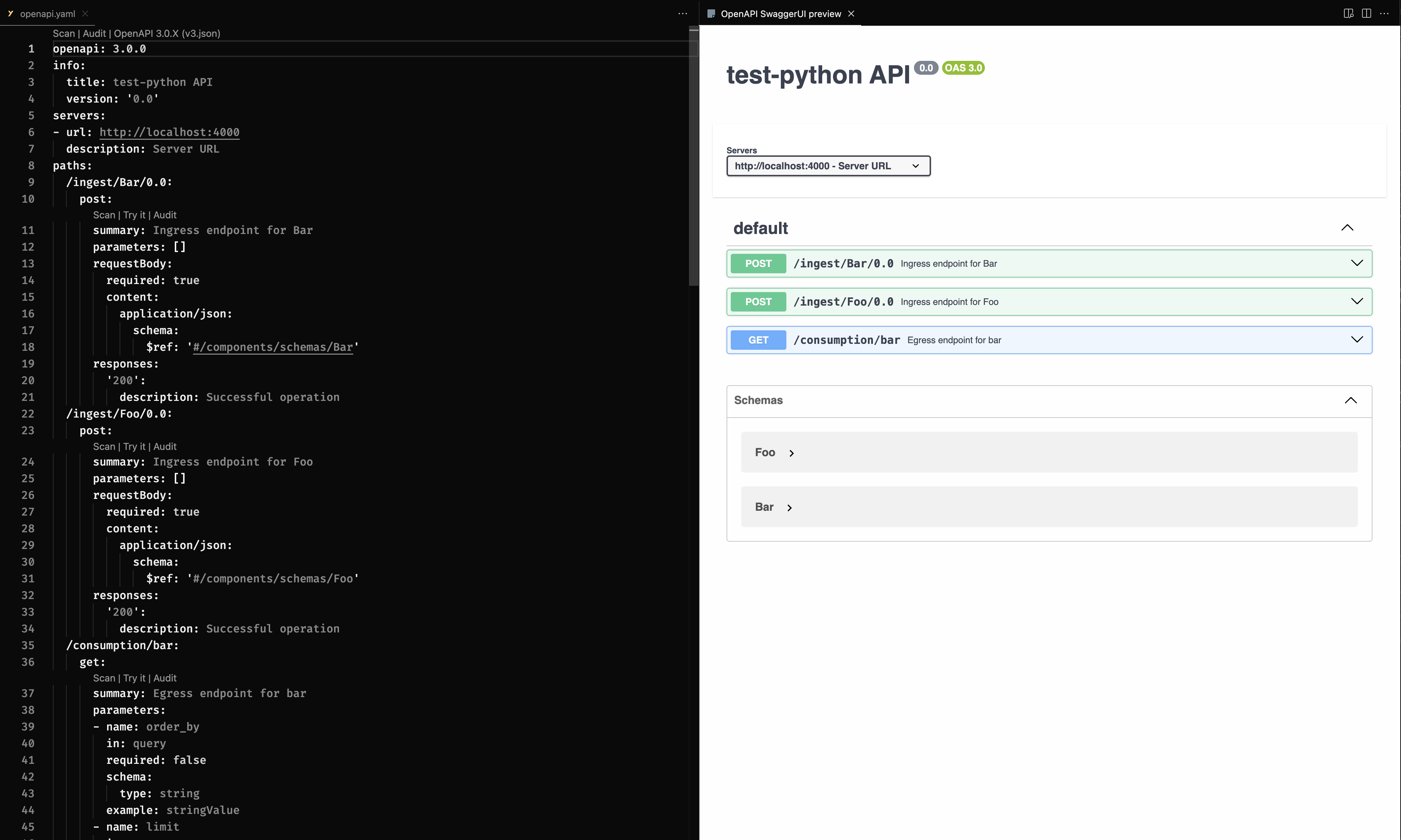
Accessing OpenAPI Documentation
Locating the File in Your Project
To view and utilize the OpenAPI documentation:
- Locate the
.moosefolder in your project. It will be in the root of your project. - Open the
openapi.yamlfile in your preferred OpenAPI viewer or editor. - Use tools like Swagger UI or Postman to explore and test the API endpoints.
- openapi.yaml
If you’re using VSCode, consider installing the OpenAPI (Swagger) Editor extension for a seamless experience.
Accessing via URL
The file is also automatically hosted on your local development server at http://localhost:5001/openapi.yaml. You can use this URL to access the OpenAPI spec from your browser.
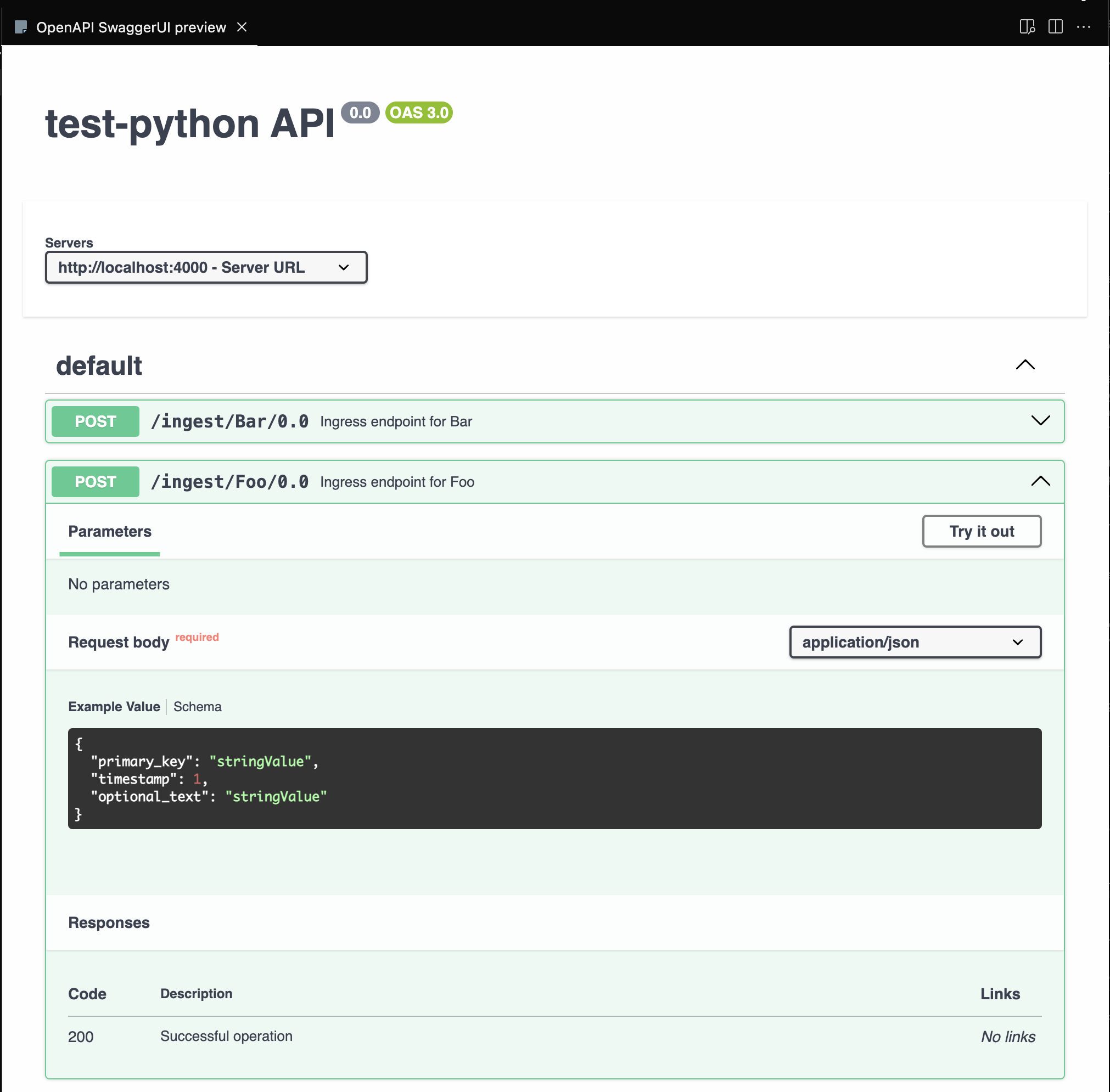
Using OpenAPI UI to Ingest Data
The OpenAPI spec includes example data for each Data Model schema, which can be used to construct requests. If using the Swagger UI, you can use the example data to construct requests by clicking the Try it out button.
Ingesting Data with Moose Workflows
Moose Workflows are a powerful way to perform ETL jobs on data. You can use the ingestion API to load data into your Data Models from your workflow tasks.
Quickstart Example
Here is an example of an ingestion workflow that generates 1000 rows of data and ingests it into the Foo Data Model:
from moose_lib import moose_data_model, Key
from dataclasses import dataclass
@moose_data_model
@dataclass
class Foo:
primary_key: Key[str]
timestamp: float
optional_text: Optional[str]import { Key } from "@514labs/moose-lib";
export interface Foo {
primaryKey: Key<string>;
timestamp: number;
optionalText?: string;
}Generate the Workflow
Run the following command:
moose-cli workflow init example_ingest_workflow --tasks "ingest"This will generate a new directory in the scripts directory called example_ingest_workflow, which contains the 1.ingest.py file:
- 1.ingest.py
npx moose-cli workflow init ExampleIngestWorkflow --tasks "ingest"This will generate a new directory in the scripts directory called ExampleIngestWorkflow, which contains the 1.ingest.ts file:
- 1.ingest.ts
Define the Ingestion Task Logic
Paste the following code into the 1.ingest.py file:
from moose_lib import task
import random
import time
import uuid
import json
import urllib.request
from datetime import datetime
@task
def generate(): # The name of your script
"""
Description of what this script does
"""
for i in range(1000):
# Generate random data
primary_key = str(uuid.uuid4())
# Generate random timestamp from last month
current_time = time.time()
one_month_ago = current_time - (30 * 24 * 60 * 60) # 30 days in seconds
timestamp = random.uniform(one_month_ago, current_time)
# Generate random optional text
words = [word.strip() for word in open('/usr/share/dict/words').readlines()] # Standard Unix word list
optional_text = f"{random.choice(words)} {i}" if i % 2 == 0 else None
# Prepare request data
data = {
"primary_key": primary_key,
"timestamp": timestamp,
"optional_text": optional_text
}
# Send POST request using only stdlib
req = urllib.request.Request(
"http://localhost:4000/ingest/Foo",
data=json.dumps(data).encode('utf-8'),
headers={'Content-Type': 'application/json'}
)
urllib.request.urlopen(req)
return {
"task_id": "generate",
"data": {
"completed_at": datetime.now().isoformat()
}
}Paste the following code into the 1.ingest.ts file:
import { TaskDefinition, TaskFunction } from "@514labs/moose-lib";
import { Foo } from "../../datamodels/models";
import fs from "fs";
import { randomUUID } from "crypto";
// Generate 1000 rows of random Foo data and ingest it into the Foo Data Model
const ingest: TaskFunction = async (input: any) => {
// Read the Unix word list
const unixWords = fs.readFileSync("/usr/share/dict/words", "utf8").split("\n");
// Get a recent timestamp within the last n_days
const getRecentTimestamp = (n_days: number) => {
const millisecondsInDays = n_days * 24 * 60 * 60 * 1000;
const intervalStartDate = Date.now() - millisecondsInDays;
return intervalStartDate + Math.random() * millisecondsInDays;
};
// Get a random word from the word list
const getRandomWord = (words: string[]) => {
return words[Math.floor(Math.random() * words.length)];
};
// Generate 1000 rows of random Foo data and ingest it into the Foo Data Model
for (let i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
const foo: Foo = {
primaryKey: randomUUID(),
timestamp: getRecentTimestamp(365),
optionalText: Math.random() < 0.5 ? getRandomWord(unixWords) : undefined,
};
await fetch("http://localhost:4000/ingest/Foo", {
method: "POST",
body: JSON.stringify(foo),
});
}
return {
task: "ingest",
data: "success",
};
};
export default function createTask() {
return {
task: ingest,
} as TaskDefinition;
}
Run the Workflow
To run the workflow, run the following command:
moose-cli workflow run example_ingest_workflownpx moose-cli workflow run ExampleIngestWorkflowExample Snippets
import { Key } from "@514labs/moose-lib";
export interface Foo {
primaryKey: Key<string>;
timestamp: number;
optionalText?: string;
}curl -X POST \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"key": "exampleKey", "value": 1, "timestamp": 1672531200}' \
http://localhost:4000/ingest/YourDataModelThe dev server runs on localhost:4000 by default. Start the server by running moose-cli dev in your terminal. Learn more
Ingestion SDK
With the OpenAPI spec, you can use tools like the OpenAPI Generator to generate an SDK for your Data Model.
If you follow their installation instructions, you can generate an SDK for your Data Model in any language that the OpenAPI Generator supports.
Assuming you are running the OpenAPI Generator CLI from the root of your Moose project, the following commands will generage an SDK for your Moose project in the moose_sdk directory:
openapi-generator-cli generate -i .moose/openapi.yaml -g python-requests -o ./moose_sdk